At CES 2025, Intel unveils new adaptive control solution,
next-gen discrete graphics and AWS virtual development
environment.
Subheadline of release dated January 7, 2025 should read:
virtual development environment (instead of virtual design
environment). First paragraph, second sentence should read: Intel®
Automotive Virtual Development Environment (VDE) (instead of Intel®
Automotive Virtual Design Environment (VDE)).
This press release features multimedia. View
the full release here:
https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20250107157568/en/
At CES on Tuesday, Jan. 7, 2025, Intel
introduced the availability of the Adaptive Control Unit (ACU),
designed for electric vehicle (EV) power trains and zonal
controller applications. The ACU U310 is a new kind of processing
unit that supports the consolidation of multiple real-time,
safety-critical and cybersecure functions, applications and domains
(X-in-1) into a single chip. (Credit: Intel Corporation)
The updated release reads:
INTEL ACCELERATES SOFTWARE-DEFINED INNOVATION WITH
WHOLE-VEHICLE APPROACH
At CES 2025, Intel unveils new adaptive control solution,
next-gen discrete graphics and AWS virtual development
environment.
What’s New: At CES, Intel unveiled an expanded product
portfolio and new partnerships designed to accelerate automakers’
transitions to electric and software-defined vehicles (SDVs). Intel
now offers a whole-vehicle platform, including high-performance
compute, discrete graphics, artificial intelligence (AI), power
management and zonal controller solutions alongside the Intel®
Automotive Virtual Development Environment (VDE) co-developed with
Amazon Web Services (AWS). Intel’s approach addresses automakers’
cost and performance scalability challenges, enabling faster, more
efficient and more profitable SDV development and deployment.
“Intel automotive is bringing innovative
solutions that reduce cost in the SDV revolution. Our whole-vehicle
approach, combined with cloud integration, delivers a complete
solution that drives down total cost of development and deployment
while empowering automakers to build the future of mobility faster,
more efficiently and more profitably.” -- Jack Weast, Intel Fellow,
vice president and general manager of Intel Automotive
Why a Whole-Vehicle Platform Matters: Intel’s
whole-vehicle platform reduces inefficiencies of traditional
fragmented approaches to vehicle architectures. By optimizing the
entire vehicle’s electrical/electronic architecture, Intel drives
significant cost reductions and performance improvements.
Supporting this platform, Intel introduced the availability of
the Adaptive Control Unit (ACU), designed for electric vehicle (EV)
power trains and zonal controller applications.
About the Adaptive Control Unit: The ACU U310 is a new
kind of processing unit that supports the consolidation of multiple
real-time, safety-critical and cybersecure functions, applications
and domains (X-in-1) into a single chip. Traditional time and
sequential processing-based micro and zonal controllers struggle to
handle multiple workloads due to limited deterministic processing
capabilities. In contrast, Intel’s new family of ACU devices
integrates a flexible logic area that offloads real-time control
algorithms from the CPU cores, ensuring reliable performance,
freedom from interference (FFI) and deterministic data delivery
even when consolidating multiple microcontroller workloads into a
single zonal MCU. This dual-brain approach enables greater workload
consolidation, lowers cost, and enhances safety, cybersecurity and
performance.
When used in an electric vehicle power train, the ACU U310
supports advanced algorithmic solutions that reduce vehicle energy
demand from the battery, automatically adapting high voltage and
control frequencies to individual driver styles and road
conditions. The ACU reduces cost per kilowatt and enhances energy
efficiency, allowing the vehicle to reclaim up to 40 percent of the
power train system energy losses, delivering a 3% to 5% efficiency
boost during the Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure
(WLTP). This translates to increased range, faster charging and a
more responsive driving experience while significantly reducing
per-vehicle bill of materials (BOM), electric motor size and
battery costs compared to traditional approaches.
- Stellantis Motorsports selected Intel as a key
technology partner and adopting the Adaptive Control technology
into its next-generation inverter control for enhanced performance
and efficiency in competitive racing environments. In this
implementation, the Intel technology will control the electric
motor and recover energy during braking phases. The inverter plays
a crucial role during a Formula E race, where any gain in
efficiency is transformed into a precious competitive
advantage.
- Karma Automotive announced support for Intel’s ACU,
showcasing an Intel co-branded inverter featuring Optimal Pulse
Pattern control algorithms to improve efficiency and enable four
unique driving profiles, including innovative features like Torque
Ripple Reduction and Range Boost.
The ACU’s programmability allows it to serve as a
first-of-its-kind software-defined zonal controller, adapting to
different vehicle topologies and applications. This flexibility
streamlines the transition to software-defined vehicles, simplifies
supply chains and reduces the complexity of the vehicle BOM.
How Next-Gen Architecture is Enhanced with AI Inside:
Building on Intel’s first-generation AI-enhanced SDV
system-on-chips (SoCs), Intel announced the upcoming
second-generation Intel® Arc™ B-series Graphics for Automotive set
for production by the end of 2025. This solution provides the
high-performance compute needed for more advanced in-vehicle AI
workloads, next-generation human-machine interface (HMI) engines,
and immersive in-vehicle experiences and AAA PC gaming. Paired with
an Intel AI-enhanced SDV SoC, it delivers scalable performance for
complex AI tasks, supported by the vast Intel AI ecosystem.
How Intel and AWS Revolutionize Automotive Software
Development: Intel and AWS introduced the Intel Automotive
Virtual Development Environment on AWS, a groundbreaking approach
that ensures true hardware and software parity from cloud to car.
This new offering addresses challenges throughout the vehicle
development life cycle, enabling engineers to seamlessly switch
between virtual and physical hardware setups. It integrates Intel®
Xeon® processor-based Amazon EC2 instances and, for the first time,
incorporates Intel’s Automotive SDV SoCs within the AWS
environment, eliminating the need for expensive electronic control
unit (ECU) simulators or developer boards. This collaboration
provides a unified solution that accelerates innovation, reduces
R&D costs and speeds time-to-market.
About Intel’s System-Level Advantage: Intel's
whole-vehicle approach delivers numerous benefits to automakers,
including cost reductions, enhanced vehicle performance,
streamlined development, improved energy efficiency, seamless AI
integration and faster time-to-market – all supported by Intel’s
globally balanced supply chain.
More: Intel at CES 2025 | Intel Auto Keynote Explores
Software-Defined Future (Video)
About Intel
Intel (Nasdaq: INTC) is an industry leader, creating
world-changing technology that enables global progress and enriches
lives. Inspired by Moore’s Law, we continuously work to advance the
design and manufacturing of semiconductors to help address our
customers’ greatest challenges. By embedding intelligence in the
cloud, network, edge and every kind of computing device, we unleash
the potential of data to transform business and society for the
better. To learn more about Intel’s innovations, go to
newsroom.intel.com and intel.com.
© Intel Corporation. Intel, the Intel logo, and other Intel
marks are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries.
Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of
others.
View source
version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20250107157568/en/
Marcie Miller 1-480-319-4629 marcie.m.miller@intel.com
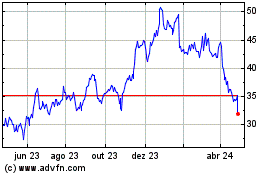
Intel (NASDAQ:INTC)
Gráfico Histórico do Ativo
De Dez 2024 até Jan 2025
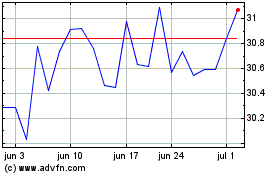
Intel (NASDAQ:INTC)
Gráfico Histórico do Ativo
De Jan 2024 até Jan 2025